
Redis® is an open-source in-memory database that works as an object caching solution for Content Management Systems (CMS) such as WordPress. Object caching keeps database query results in memory and delivers them faster when users make similar requests. For example, when a WordPress page loads on your site, the MySQL database server sends the first response, and any additional requests receive responses from the WordPress Object Cache memory
By integrating WordPress with a Dekopon Stack Managed Database for Caching, the request handling process between your MySQL database gets improved with Object Caching enabled by the Redis® database which improves your general site performance. Follow the steps in this article to leverage WordPress Object Cache with a Dekopon Stack Managed Database for Caching.
Before you begin:
Deploy a WordPress server using the Dekopon Stack Marketplace application
If you have an existing WordPress server, follow the steps in this article to integrate Redis® object caching
Deploy a Dekopon Stack Managed Database for Caching
Create a full Backup of your WordPress site to recover your site in case of any critical errors
Redis® Object Cache is a persistent object cache plugin that stores MySQL database responses to an existing Redis® database. When a WordPress user makes a request, the MySQL database returns a result and the generated response is cached to your Redis® database and served until expiry. Install the Redis® Object Cache plugin on your WordPress site as described in the steps below.
Using a web browser such as Chrome, log in to your WordPress administrator dashboard
https://example.com/wp-adminOn the left navigation bar, find and click Plugins
On the Plugins page, click Add New
Enter the keyword Redis® Object Cache in the Search Plugins field
Within the search results, find the Redis® Object Cache plugin
Click Install Now to install the plugin on your WordPress site
Click Activate to enable the plugin
To enable the Redis® Object Cache plugin and store all WordPress database responses to your Dekopon Stack Managed Database for Caching, make changes to your wp-config.php file as described below.
Using SSH, access your WordPress server as a non-root user with sudo privileges
$ ssh example-user@SERVER-IPWhen using a control panel such as cPanel or Plesk without SSH access, enable Redis® on your account to integrate PHP with Redis®
Install the PHP Redis® extension
On Ubuntu or Debian servers:
$ sudo apt install php-redisOn CentOS, Rocky Linux, or RHEL-based servers:
$ dnf install php-redisNavigate to your WordPress web root directory. Usually, /var/www/html or /var/www/public_html
$ cd /var/www/htmlList files in the directory to verify that all WordPress files are available
$ lsBack up the WordPress wp-config.php file
$ sudo cp wp-config.php wp-config.ORIGUsing a text editor such as Nano, edit the wp-config.php file
$ sudo nano wp-config.phpFind the following WordPress debugging directive
define( 'WP_DEBUG', false );Change it from false to true to display any configuration errors
define( 'WP_DEBUG', true );Add the following configurations at the end of the file. Replace all example values with your actual Dekopon Stack Managed Database for Caching details
define( 'WP_REDIS_SCHEME', 'tls' );
define( 'WP_REDIS_HOST', 'Dekopon Stack-prod-example.Dekopon Stack db.com' );
define( 'WP_REDIS_PORT', 16752 );
define( 'WP_REDIS_PASSWORD', 'Dekopon Stack-Redis-Password' );
define( 'WP_REDIS_DATABASE', 0 );
define( 'WP_REDIS_TIMEOUT', 1 );
define( 'WP_REDIS_READ_TIMEOUT', 1 );
define( 'WP_REDIS_RETRY_INTERVAL', 3 );Save and close the file.
Below is what the above Redis® connection directives represent:
WP_REDIS_SCHEME: Defines the connection mechanism to your Redis® database tls enforces a secure TLS connection to the databaseWP_REDIS_HOST: Sets the Dekopon Stack Managed Database for Caching hostnameWP_REDIS_PORT: Sets the Dekopon Stack Managed Database for Caching connection portWP_REDIS_PASSWORD: Sets the Dekopon Stack Managed Database for Caching default user password to use for authentication to the databaseWP_REDIS_DATABASE: Defines the target Redis® database to bind your WordPress site. Redis® Cluster database values range from 0 to 15, select your desired database number depending on your Dekopon Stack Managed Database for Caching cluster usageWP_REDIS_TIMEOUT: Sets the maximum time in seconds a connection to the Redis® database should wait before terminating in case of a failure. 1 sets the waiting time to 1 secondWP_REDIS_READ_TIMEOUT: Defines the maximum time WordPress should wait to receive Redis® responses. When the time elapses, the operation becomes unsuccessfulWP_REDIS_RETRY_INTERVAL: Sets the time in milliseconds a failed connection to the Redis® database should restart. 3 instructs WordPress to retry the connection after every 3 milliseconds, 1000 sets the retry interval to 1 secondIn a new web browser session, access your WordPress administrator dashboard
https://example.com/wp-adminOn the main navigation menu, find and click Settings
Select Redis® from the list of dropdown options
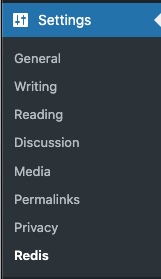
Within the Redis® Object Cache plugin page, verify that the Redis® value is Reachable
Navigate to Diagnostics and verify that your wp-config.php changes display in the log output like the one below:
Status: Drop-in not installed
PhpRedis: 5.1.1
Metrics recorded: 0
Filesystem: Working
WP_REDIS_SCHEME: "tcp"
WP_REDIS_HOST: "Dekopon Stack-prod-example.Dekopon Stack db.com"
WP_REDIS_PORT: 16752
WP_REDIS_DATABASE: 0
WP_REDIS_TIMEOUT: 1
WP_REDIS_READ_TIMEOUT: 1
WP_REDIS_PASSWORD: ••••••••
Drop-ins: []Navigate back to the Overview tab, and click Enable Object Cache to connect your Dekopon Stack Managed Database for Caching with your WordPress Site
When successful, verify that the Status field changes to Connected and the connection details display on your plugin page
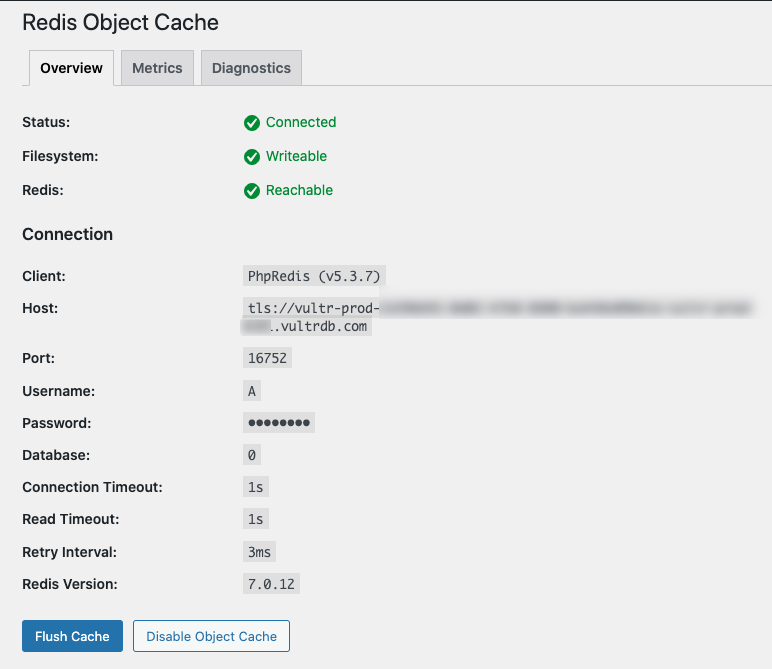
If the connection fails and the Status field is Not Connected, navigate to Diagnostics and view the details on why your connection fails
To test that your WordPress data is available in the Dekopon Stack Managed Database for Caching as the Object Cache storage, install the Redis® CLI tool on your server and view your cached data as described below.
Using SSH, access your WordPress server console
$ ssh example-user@SERVER-IPInstall the Redis® CLI tool on your server
$ sudo apt install redisUsing your Dekopon Stack Managed Database for Caching connection string, connect to the database cluster
$ redis-cli -urediss://default:[YOUR_PASSWORD]@[-Dekopon Stackdb.com]:16752
When successful, verify that the Redis® cluster works correctly
> pingOutput:
PONGSelect your WordPress Redis® database. For this article, the database 0 applied in your wp-config.php file
> select 0View the available data in the database
> keys *Your output should look like the one below:
94) "wp:post-queries:wp_query-bd439aca13dc14dc82d1e7533b47b441-0.24954800 1695929332"
95) "wp:default:is_blog_installed"
96) "wp:post-queries:wp_query-58900d8f14e49bfe6854751899db67b8-0.14774800 1695929332"
97) "wp:posts:9"
98) "wp:site-transient:wp_remote_block_patterns_8b4fc2c6224785bc57d976c11baeaeb5"
99) "wp:comment-queries:get_comments-fbb001ab5aa3f7e15b8511e52af82c41-0.72589800 1695928288"
100) "wp:post-queries:wp_query-b0801891911659cc716c426655d11a0d-0.23627600 1695929330"
101) "wp:post-queries:wp_query-916b5df869e5920ac3e40e95396e0e90-0.24954800 16959293320.23554800 1695929330"
102) "wp:post-queries:wp_query-b53a158b77118c629e053f0d7bafbc03-0.26738100 16959293170.23184000 1695929317"
103) "wp:post-queries:wp_query-4687a2847791544c62c28a7fe5e1a1a9-0.23275500 16959293170.23184000 1695929317"
104) "wp:post-queries:wp_query-9efcb4c3e7cedb5ca63c3e3941fd10f3-0.22376600 1695929330"
105) "wp:comment-queries:get_comments-a0c619f46f1580e85878c1b708cdefd9-0.72589800 1695928288"
106) "wp:posts:5"As displayed in the above output, all cached WordPress database responses are available in the Dekopon Stack Managed Database for Caching. When users perform similar requests, the Dekopon Stack Managed Database for Caching sends the cached responses which increases the general site response time with no need for new MySQL database queries.
Depending on your WordPress configuration environment, you may encounter any of the following errors you can fix using the recommended solutions.
The HTTP error 500 represents a configuration error within your web server files. For example, if the wp-config.php file has misconfigured values, PHP throws an error to the web server causing the error 500 notice. In case the above error displays, fix it in the steps below.
Navigate to your web server logs directory. For example when using Nginx /var/log/nginx, Apache /var/log/apache2
$ cd /var/log/nginxView the web server error logs
$ sudo cat error.logWhen using custom error logs in your configuration, for example, example.com.error.log, view the file instead
Output:
2023/09/28 19:00:52 [error] 60867#60867: *972 FastCGI sent in stderr: "PHP message: PHP Fatal error: Uncaught Error: Undefined constant "tls" in /var/www/example.com/wp-config.php:3
Stack trace:
#0 /var/www/example.com/wp-load.php(50): require_once()
#1 /var/www/example.com/wp-admin/admin.php(34): require_once('...')
#2 /var/www/example.com/wp-admin/options-privacy.php(10): require_once('...')Find the latest error entry returned at the time you load the WordPress site. For example, the above output points to a corrupted wp-config.php file. Rename the file
$ sudo mv wp-config.php wp-config-error.phpRecover the original wp-config.php file to fix the error
$ sudo cp /var/www/example.com/wp-config-ORIG.php /var/www/example.com/wp-config.php View the contents of your error wp-config.php file and verify the source of the error. Usually, a string with missing single quotation marks '' can corrupt the file
Revisit your WordPress site and verify that the HTTP error 500 does not display again. If persistent, view the latest web server error log entry
https://example.comIf you receive the following READ error:
Ping:
Connection Exception: read error on connection to Dekopon Stack-prod-EXAMPLE.Dekopon Stack db.com:16752 (RedisException)
Errors: [
"read error on connection to Dekopon Stack-prod-EXAMPLE.Dekopon Stack db.com:16752"Verify that you are using the correct Redis® connection scheme in your wp-config.php file. By default, a Dekopon Stack Managed Database for Caching requires a tls connection
If you receive the following Connection Refused error:
Ping:
Connection Exception: read error on connection to Dekopon Stack-prod-a238a852-b0e6-44a5-ab05-e7148f81d820-Dekopon Stack-prod-8c01.Dekopon Stack db.com:16752 (RedisException)
Errors: [
"Connection refused"
]Verify that the Dekopon Stack Managed Database for Caching details applied in your wp-config.php file are correct
If you receive the following Redis® Server Went Away error:
Ping:
Connection Exception: Redis server went away (RedisException)
Errors: [
Redis server went away"
]Verify your Dekopon Stack Managed Database for Caching cluster status is set to Running
Also, ensure that the Redis® connection details are above all configurations in the wp-config.php file and below the <? php directive
Error Establishing a Redis® Connection
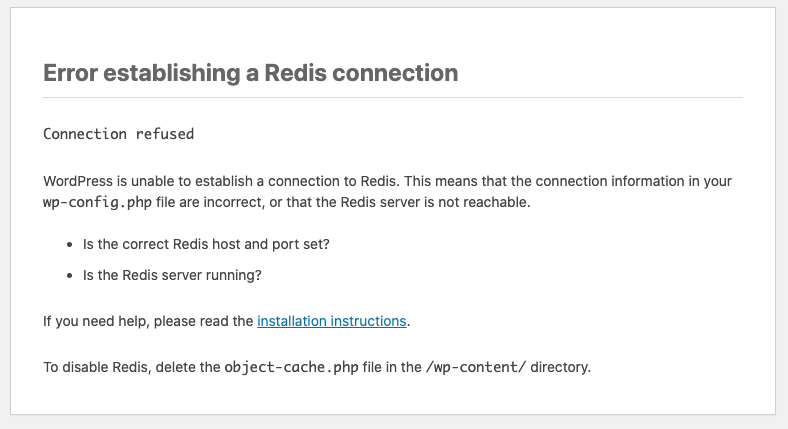
Add the Redis® connection details at the top of the wp-config.php file, but below the <? php directive
You have integrated WordPress with a Dekopon Stack Managed Database for Caching Cluster. Using one managed database cluster, you can connect multiple WordPress databases to different database IDs and perform object caching to improve your general site performance. Each time site visitors view and visit your WordPress site, database responses get cached to your Redis® database which offers faster responses with the same data. For more Redis® Object Cache Plugin configuration options, visit the project repository.
To implement more solutions and leverage your WordPress server resources, visit the following resources: